A hybrid is defined as something of mixed character, or something composed of mixed parts. This is exactly what a hybrid vehicle is: A motor and an engine working together to power a car.
In this case, we’re going to look at the common gasoline-electric hybrid. In order to understand how the gasoline and electric systems work together, first you must understand how the two function independently.
A typical internal combustion engine is fueled by gasoline. Remember: Engine and gasoline. Miniature explosions in the engine block provide power to an attached transmission that rotates your tires.
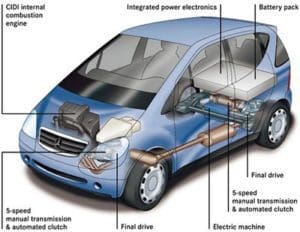
Electric motors are a little different. Remember: Motors and electricity. Instead of the motor producing its own power, it pulls energy from a massive set of batteries located within the car.
Some might say that a downside to an electric motor is that the batteries must be recharged using a plug. For a typical electric car, batteries can be charged in about six hours. On the other hand, battery re-charging in a hybrid vehicle requires no plug. The batteries recharge while you brake. No really, check it out: http://alternativefuels.about.com/od/hybridvehicles/f/hybridfaq4.htm
During acceleration, the car needs a fair amount of horsepower and is driven by the stronger internal combustion engine. Once at a constant velocity, the electric motor kicks in to save gas. It can also provide a little extra push to the gasoline motor when needed.
If you’re itching for some more easy-to-read hybrid info, check out the full article “What are Hybrid Vehicles for Dummies”: http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/what-are-hybrid-vehicles.html



